Copilot + Excel = Your Data Superpower

Copilot in Excel simplifies data analysis by enabling you to search for and import data from Word, PowerPoint, PDF documents, or other Excel files into your spreadsheets. Save time and gain insights with this powerful tool.
Search and import data with Copilot in Excel
Data analysis is a critical yet challenging task for many business professionals, as creating and preparing data, then gaining insights from it and conducting advanced analyses, can be time-consuming and complex.
Copilot in Excel can help! We’re thrilled to announce that Copilot in Excel can now reference Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and PDF files, making the entire data collection and analysis process faster, simpler, and more intuitive.
This new capability works for gathering information such as:
- Web content: You can seamlessly search the web directly within Copilot in Excel to find public information like dates, statistics, and more without disrupting your workflow. For instance, you can look up a list of countries and their exchange rates, and easily paste these results into a table.
- Internal content: For example, you can ask Copilot in Excel to list the announcements from a newsletter drafted in Word, and Copilot will respond with a list that you can insert into a new spreadsheet.
- Organizational information: You can ask Copilot for all the employees who report to a specific manager and insert this list into a spreadsheet.
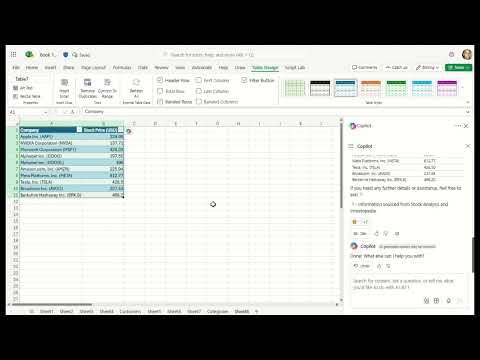
- Data from another Excel file: One of our top user requests is to import data from another Excel file. This is possible with Power Query, but doing so takes time and knowledge – not to mention, searching for the right file can be frustrating. Now you can ask Copilot for help finding and importing a table from an Excel file using everyday language. For example, say you want to add budget details from another Excel spreadsheet to your sales team table: You can describe the data that you need, and Copilot will help you import it. Because this import is powered by Power Query, it brings precise data directly from your organization’s data sources as a refreshable connection. As data is updated in the budget file, it also updates in your sales team table.
How it works
- On the Home tab in Excel, select Copilot.
- Ask Copilot a question about the data you are looking for.
- Ask follow-up questions to Copilot’s responses until you’re happy with the results!
Video provider requires cookies to play the video. Accept to continue or watch it directly on the provider’s site.Accept
NOTE: For results that are from external data, make sure you see reference(s) at the end of the response.
Scenarios to try
Try prompting Copilot in Excel with:
- “Search the web for an itinerary for a month-long trip to Europe in a table format.”
- “Search the web for a list of 15 intermediate-level vocabulary words in Spanish and their translations.”
- “Show me next week’s meetings and to-do items in a table.”
- “List yesterday’s emails in a table, with sender, subject line, and importance.”
Known limitations
- Importing refreshable data is only supported for Excel files with tables, stored on your SharePoint or OneDrive.
- Addressing workbook data and asking for external data simultaneously is not fully supported yet.
Requirements
To use this feature, you must have:
- a Copilot license (get more details on licenses for consumers and for businesses).
- a stable internet connection.
- web search enabled (for web searching).
If Copilot responds that it can’t access your organizational data, verify if Restricted SharePoint Search is turned on (for Enterprise search).